In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of the Antifungal Activity of Apx001a/Apx001 Against Candida
Abstract
Candida auris is an emerging multidrug-resistant yeast that has been responsible for invasive infections associated with high morbidity and mortality. C. auris strains often demonstrate high fluconazole and amphotericin B MIC values, and some strains are resistant to all three major antifungal classes. We evaluated the susceptibility of 16 C. auris clinical strains, isolated from a wide geographical area, to 10 antifungal agents, including APX001A, a novel agent that inhibits the fungal protein Gwt1 (glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored wall transfer protein 1). APX001A demonstrated significantly lower MIC50 and MIC90 values (0.004 and 0.031 μg/ml, respectively) than all other agents tested. The efficacy of the prodrug APX001 was evaluated in an immunocompromised murine model of disseminated C. auris infection. Significant efficacy (80 to 100% survival) was observed in all three APX001 treatment groups versus 50% survival for the anidulafungin treatment group. In addition, APX001 showed a significant log reduction in CFU counts in kidney, lung, and brain tissue (1.03 to 1.83) versus the vehicle control. Anidulafungin also showed a significant log reduction in CFU in the kidneys and lungs (1.5 and 1.62, respectively) but did not impact brain CFU. These data support further clinical evaluation of this new antifungal agent.
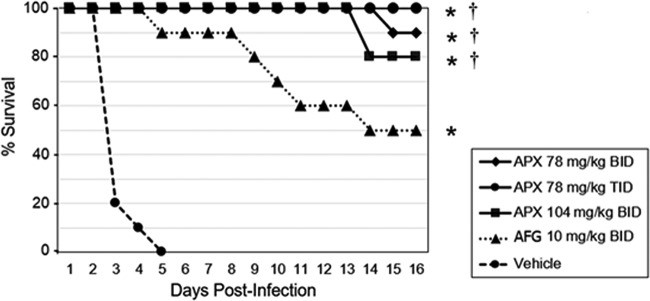
Figure 1
Survival curves in mice infected with C. auris CBS 12766. Treatments were administered by i.p. injection (n = 10/group): APX001 at doses of 78 mg/kg BID, 78 mg/kg TID, or 104 mg/kg BID; 10 mg/kg anidulafungin BID; or vehicle BID. Treatment began 2 h postinoculation and continued for 7 days. Survival was monitored until day 16. Survival was plotted by Kaplan-Meier analysis, and differences in the percent survival among groups were analyzed by the log-rank test and the Fisher exact test, respectively. Abbreviations: APX, APX001A; AFG, anidulafungin. *, P ≤ 0.0001 versus vehicle control; †, P ≤ 0.05 versus anidulafungin.
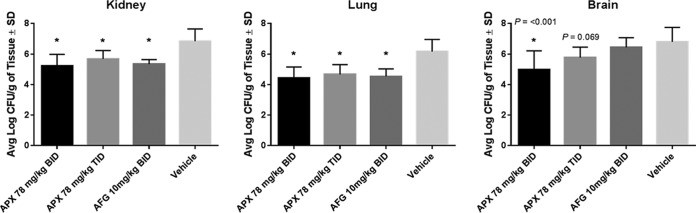
Figure 2
Reduction in fungal burden in the mouse kidneys, lungs, and brains at 48 h postinfection with C. auris CBS 12766. Treatments were administered by i.p. injection (n = 5/group): APX001 at doses of 78 mg/kg BID or 78 mg/kg TID; 10 mg/kg anidulafungin BID; or vehicle control BID. Treatment began at 2 h postinoculation and continued for 2 days. Animals were sacrificed at 48 h, and the fungal burden was determined. Differences in mean CFU in mouse kidneys, lungs, and brains were compared to the vehicle control using a one-way ANOVA with a post hoc Tukey test. Abbreviations: APX, APX001; AFG, anidulafungin. *, P ≤ 0.001 versus control.